Services
-

Family Medicine
The mission of Trident Health Center is to live up to the definition of family medicine
-

Sports Medicine
Michael Jordan once said, “Just play. Have fun. Enjoy the game.”
-

Pediatrics
Frederick Douglass once said, “It is easier to build strong children than to repair broken men” or women.
-

Geriatrics
The playwright, George Bernard Shaw, once said that “Youth is wasted on the young.”
-

Annual Physicals
Getting regular and annual physicals is a key component of prevention and early diagnosis which is a hallmark of family medicine. Schedule today for an annual physical to get checked and make use of the opportunity to treat problems early and maintain health for life.
-
Diabetes
Diabetes Mellitus is a metabolic disorder resulting in high blood sugars that has been known from ancient times.
-
High Blood Pressure Management
Hypertension is often referred to a “silent killer” because of its usual lack of symptoms until presentation with a major event.
-
Pulmonary Embolism/DVT
Venous thromboembolism is a medical term that describes a blood clot that forms in a vein.
-
High Cholesterol
When Aristotle once said “moderation in all things”, he might have been talking about cholesterol in the body.
-

Asthma
Asthma is characterized by recurrent (sometimes constant) symptoms of shortness of breath, wheezing, and cough.
-
Thyroid Disorder
The thyroid is an important organ that controls the metabolic function of the body.
-
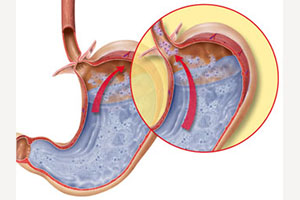
Acid Reflux/Ulcer Disease
Stomach problems whether due to heartburn, reflux, or ulcer disease can be a serious problem that affects the ability of individuals to eat, sleep, etc. An evaluation for the cause of the problem is critical along with a management of the symptoms.
-

Vitamin Injections
Vitamin deficiencies are a common occurrence in society. At Trident Health Center, we offer vitamin injections for the treatment of medical abnormality and for the sake of wellness. Here is a description of various vitamins and how their deficiencies can affect the body.
-

Allergy Testing
Allergies are caused by a hypersensitive reaction from the immune system to something in the environment that does not cause a reaction in most people.
The common symptoms of allergies are:
• Rash
• Itchy eyes
• Runny nose
• Shortness of breath
• Drowsiness
• Headaches
• Nausea
Placental Allografts
The placenta is a maternal-fetal organ that develops from the fetus and attaches to the uterus during pregnancy. The placenta is responsible for, among other things, providing the growing fetus with oxygen and nutrients while at the same time removing toxins.1 It also serves as a barrier between maternal and fetal compartments. Once the baby is born, the placenta detaches from the uterine wall and is expelled from the body. Placental tissue can be harvested after a healthy, concluded birth and then processed into a human, placental tissue allograft.
